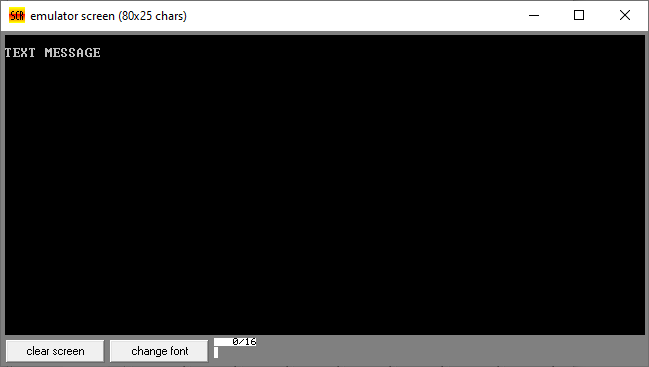
This program prints simple text on screen in 8086 assembly language. Click to download the code
Printing a text in assembly language is very easy.
In assembly language we need to build a logic and then write a
program. In this program we only need to print a simple message for which we
have written this code.
1.
First we write the title of program so that we can understand
the purpose of program
TITLE TEXT_MESSAGE
2.
Then we define the model, model is the part of program which
tells assembler which model we need to use for our program. In this program we
are using SMALL, but there are many like
TINY, SMALL and LARGE
.MODEL SMALL
3.
Then we define the stack of program. STACK usually tells
assembler that how much bytes we need to use for our DATA SEGMENT (explained
later). In this program we have used 100 bytes in hexadecimal
.STACK 100H
4.
Now comes the DATA SEGMENT, which, we define as .DATA. in DATA
SEGMENT we store our variables and
temporary data. For example our temporary bytes. In this program we have stored
an array of characters containing our message.
That’s how you define a array of characters (string) in
assembly.
NAME
|
TYPE
|
“MESSAGES$”
|
MSG
|
DB
|
0AH, 0DH, "TEXT MESSAGE$"
|
MSG is the name of message you can have any name, DB is DEFINE
BYTE (will be explained further in variables section) and then our text
message. You notice 0AH and 0DH these bytes are for carriage return and line
feed, now the message which is in quotes, be careful for dollar sign ($), which
is string terminator, do not forget to add it after every message.
5.
After setting up DATA SEGMENT, CODE SEGMENT starts, which tells
assembler that our program has been started. We define CODE SEGMENT same as we
defined DATA SEGMENT.
.CODE
In the code segment first we define a label from which our
program starts, in this program we have defined MAIN: with colon. Then we move
starting address of DATA SEGMENT by using AX register in to DS register (will
be explained later programs). First move address to AX register then mov it
back to DS register.
MOV AX, @DATA
MOV DS, AX
6.
To print the message we need to move its address to DX register
there are two way to do it but we will use OFFSET command to do it. After moving
address to DX register we store 09H byte in AH register to tell assembler that
we want to print a string. Now we invoke interrupt service routine by using INT
21H
MOV DX, OFFSET MSG
MOV AH, 09H
INT 21H
7.
Now that we have completed the task of string printing we need
to tell assembler that where to end the program for this we simply define another
label name EXIT: with colon and move 4CH byte in AH register and invoke INT 21H
after this we use END MAIN (without colon)
EXIT:
MOV AH, 04CH
INT 21H
END MAIN
Here is the complete program.