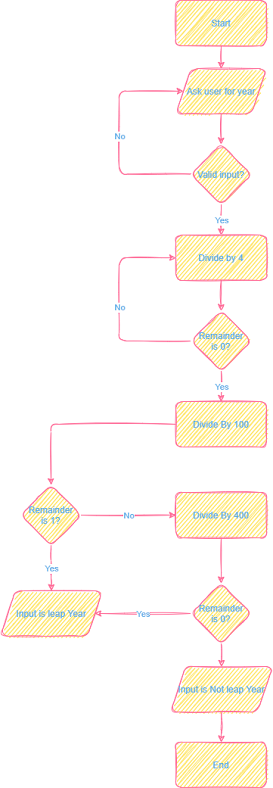
In this tutorial, we will learn how to calculate leap year with a simple python script. First, we need to understand the rules behind a year being a leap year to write the code. The steps to calculate leap year are following
If the year is evenly divisible by 4, go to step 2. Otherwise, go to step 5.
If the year is evenly divisible by 100, go to step 3. Otherwise, go to step 4.
If the year is evenly divisible by 400, go to step 4. Otherwise, go to step 5.
The year is a leap year (it has 366 days).
The year is not a leap year (it has 365 days).
For more information and detailed examples, we can read This article.
To write a python script, we will create a flowchart of the rules as mentioned earlier.
After creating a flowchart, we can start writing python code.
Step 1: Ask User for Input
To allow users to input a value, we need to add an 'input' statement in our program. The 'input' statement displays a string and returns the text input by users, so we need to store it in a variable. We will define a variable named 'user_input', so our first statement becomes this.
user_input = input(“"Enter a Year: ")
However, the input statement returns any value input by the user as text. To handle this, we add the 'int' statement before the 'input' statement.
user_input = int(input(“"Enter a Year: "))
Step 2: Process the Input
Once the user has input, we have our value stored in a variable name 'user_input' we can process it as 'user_input'. First, we divide the 'user_input' by 4. Please keep in mind that we will use the modulus division method because we want to check if the remainder is 0 or not.
If the remainder is 0, then we divide it by 100. However, before we check the remainder of the division of 100, if we re-read Rule 2 mentioned above, we can see if we do not check the remainder of the division of 100 for 0. However, for 1, we can skip step 3 and directly go to step 4. So our code becomes
if (year%4==0):
if(year%100==1):
print(f"{year} is a leap year!!")
**notice the indentation? Keep it that way because python uses indentation to nest statements.
We have used two 'if' statements to check the leap year, but when both the 'if' statements are false, we will divide 'user_input' by 400 and check the remainder for 0. We add 'else statement for this purpose.
def leap_check(year):
if (year%4==0):
if(year%100==1):
print(f"{year} is a leap year!!")
else:
if(year%400==0):
print(f"{year} is a leap year!!")
Then we declare everything else as not a leap year.
if (year%4==0):
if(year%100==1):
print(f"{year} is a leap year!!")
else:
if(year%400==0):
print(f"{year} is a leap year!!")
else:
print(f"{year} is not a leap year!!")
else:
print(f"{year} is not a leap year!!")
Now wrap up all the code in a function and call it in main.
def leap_check(year):
if (year%4==0):
if(year%100==1):
print(f"{year} is a leap year!!")
else:
if(year%400==0):
print(f"{year} is a leap year!!")
else:
print(f"{year} is not a leap year!!")
else:
print(f"{year} is not a leap year!!")
Step 3: Display outputs
The 'print' function will display the and data already used in the 'if' statement.
user_year = int(input("Enter a Year: "))
leap_check(user_year)
If you find any difficulties in this code or tutorial, please click here or visit Ask For Help.
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------